

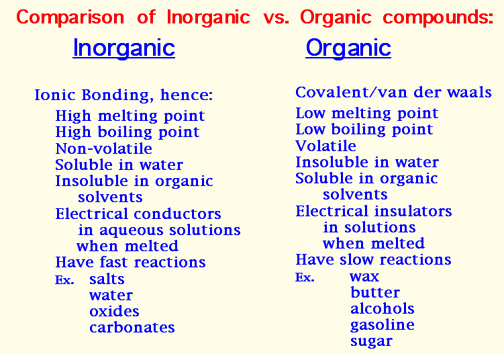
The substance was urea, the end product of protein metabolism.


General Types of Organic Compounds
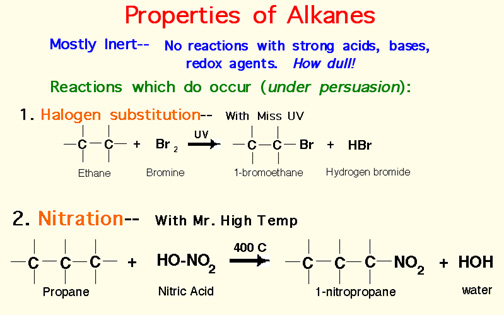
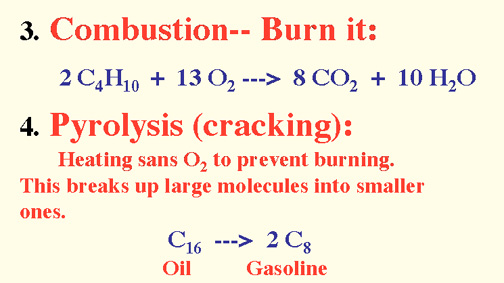
The Alkanes
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons (no double nor triple bonds).
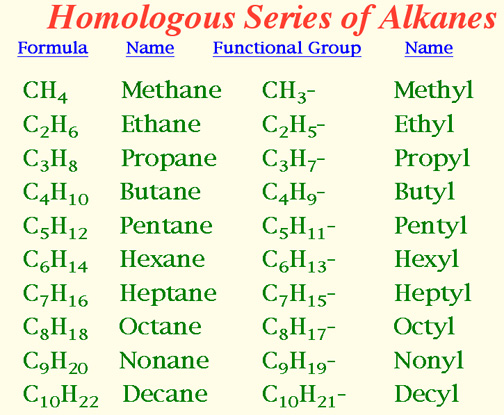

Naming Alkanes


The substance was urea, the end product of protein metabolism.



General Types of Organic Compounds
The Alkanes
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons (no double nor triple bonds).


Naming Alkanes
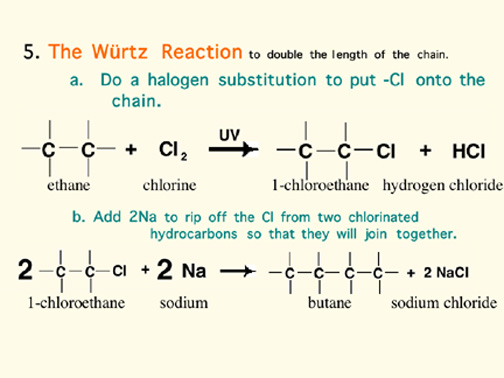
Number the longest chain such that side groups have smallest numbers.
Locate the side groups and name them.
End the compound in ane.

Naming Alkenes
Number the longest chain starting at the end closer to the double bond.
Attachments are done as those of the alkanes.
Give the number of the carbon on which the double bond begins.
The ending is ene.
Properties of Alkenes
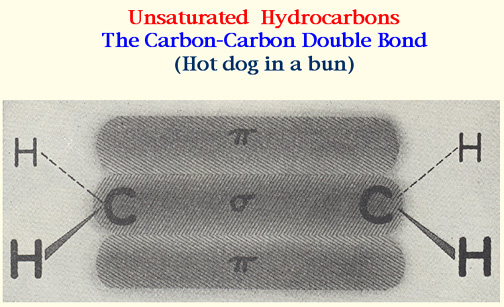
The structure of the Double Bond--
..... The Hot Dog in a Bun.
..... The carbons are closer together.
..... The double bond prevents rotation and causes Cis-Trans Isomers.
..... Alkenes are very reactive.
.......... Because…
The extra pair of electrons are not so strongly held owing to their greater distance from the nuclei. (Inverse Square Law).
The energy of the extra pair of electrons is not needed to hold the carbons together so their energy is available for reacting.
The extra pair of electrons is out where the action is. Like bumpers.
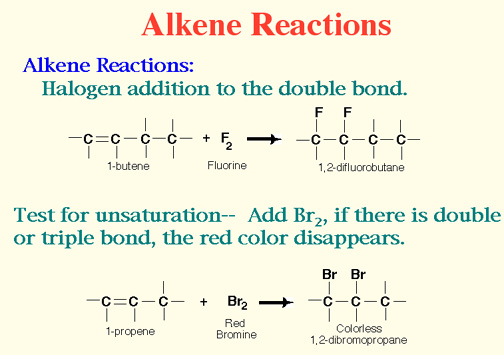
Demo: The Bromine Test for Unsaturation.
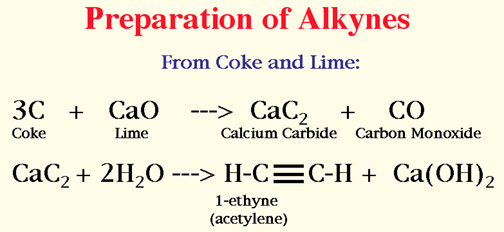
Alkynes
The structure of the Triple Bond--
..... Hot dog in a Romiso Double Bun
.......... Properties of the Triple Bond:
.......... Super Reactive!
.......... Reactions are the same as those for Alkenes? but they can happen twice.
The Model:

Naming of Alkynes
Number the longest chain starting at the end closer to the triple bond.
Attachments are done as those of the alkanes.
Give the number of the carbon on which the triple bond begins.
The ending is yne.
Demo:
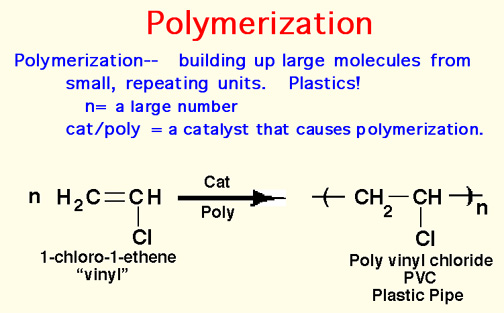
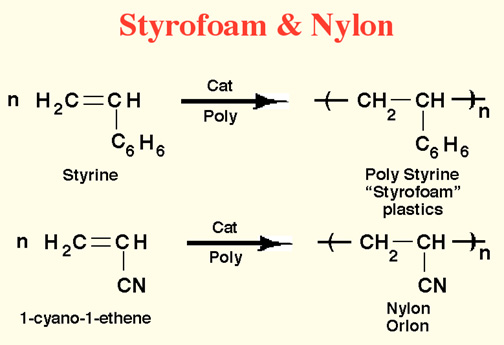

Here Endeth Organic Part 1